What is Genetics
What is Genetics?
Genetics is the branch of biology that studies genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms. It plays a crucial role in understanding how traits and characteristics are passed from one generation to the next. In the context of dogs, genetics helps us comprehend the inheritance of specific traits, such as coat color, size, and even behavior. By examining the genetic makeup of a dog, breeders can make informed decisions to enhance desirable traits and reduce the risk of hereditary diseases.
The Role of DNA in Genetics
At the core of genetics lies DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. In dogs, DNA is organized into chromosomes, which contain genes. Each gene is a segment of DNA that encodes information for a specific trait. Understanding the structure and function of DNA is essential for anyone interested in the genetics of dogs, as it provides insight into how traits are inherited and expressed.
Genes and Alleles
Genes come in different forms known as alleles. Each dog inherits two alleles for each gene, one from each parent. These alleles can be dominant or recessive, influencing how traits are expressed. For example, if a dog inherits a dominant allele for a specific coat color, that color will be expressed, even if the other allele is recessive. This interplay between dominant and recessive alleles is fundamental to understanding genetic variation in dog breeds.
Genetic Variation and Dog Breeds
Genetic variation is the diversity in gene frequencies within a population. In dogs, this variation is what leads to the wide array of breeds, each with unique characteristics. Selective breeding practices have amplified certain traits, resulting in distinct breeds with specific appearances and temperaments. Understanding genetic variation helps breeders maintain breed standards while also considering the health and well-being of the dogs.
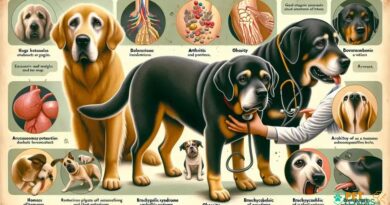
Hereditary Diseases in Dogs
Genetics also plays a significant role in the prevalence of hereditary diseases in dogs. Certain breeds are predisposed to specific genetic disorders, such as hip dysplasia, progressive retinal atrophy, and certain types of cancer. By understanding the genetic factors that contribute to these conditions, breeders can take proactive measures to reduce the incidence of hereditary diseases, ensuring healthier dogs for future generations.
Genetic Testing for Dogs
Genetic testing has become an invaluable tool for dog owners and breeders alike. These tests can identify specific genetic markers associated with various traits and health conditions. By utilizing genetic testing, breeders can make informed decisions about mating pairs, helping to reduce the risk of passing on hereditary diseases. Additionally, dog owners can gain insights into their pet’s genetic background, allowing for better care and management of potential health issues.
The Impact of Environment on Genetics
While genetics plays a crucial role in determining a dog’s traits, it is essential to recognize the impact of the environment. Factors such as diet, training, and socialization can influence how genetic traits are expressed. For instance, a dog with a genetic predisposition for aggression may not exhibit aggressive behavior if raised in a nurturing environment. Understanding the interaction between genetics and environment is vital for responsible dog ownership and breeding practices.
Ethical Considerations in Canine Genetics
As our understanding of genetics advances, ethical considerations arise regarding breeding practices and genetic manipulation. Responsible breeders prioritize the health and well-being of their dogs, avoiding practices that may lead to genetic disorders. Ethical breeding involves transparency about a dog’s genetic background and a commitment to improving the breed. As genetic technologies evolve, it is crucial to balance innovation with ethical responsibility in the canine world.
The Future of Canine Genetics
The future of canine genetics holds exciting possibilities, including advancements in gene editing and personalized medicine for dogs. As researchers continue to explore the canine genome, we may uncover new ways to enhance health and longevity in dogs. These developments could lead to more effective treatments for genetic disorders and a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between genetics and behavior. The ongoing research in this field promises to revolutionize how we approach dog breeding and care.